Wasatch Front Travel Demand Model
Since 2000, WFRC has partnered with our neighboring MPO, Mountainland Association of Governments (MAG) to develop and support a shared, regionwide travel demand model called the Wasatch Front Travel Demand Model (WF-TDM).
The WF-TDM is a modified 4-step travel model that incorporates a travel time feedback loop in  order to evaluate roadway congestion costs in its distribution of trip origins and destinations and its travel mode choice modules. The model calculates roadway volumes, travel speed indicators, transit route boardings, and regional statistics including vehicle miles traveled (VMT), vehicle hours traveled (VHT), transit/auto/non-motorized mode shares, and trip length costs.
order to evaluate roadway congestion costs in its distribution of trip origins and destinations and its travel mode choice modules. The model calculates roadway volumes, travel speed indicators, transit route boardings, and regional statistics including vehicle miles traveled (VMT), vehicle hours traveled (VHT), transit/auto/non-motorized mode shares, and trip length costs.
The current version of the WF-TDM is version 9.0.0, with version 9.0.1 and version 9.1.0 in production. For more information regarding model versions, please reference the online documentation.
Versions 9.0.0 and 8.3.2 of the WF-TDM were used to support forecasting and scenario evaluation during the development of the 2023-2050 Regional Transportation Plan (RTP). Version 9.0.0 was adopted (May 25, 2023) as the official version, coinciding with the formal adoption of the 2023-2050 RTP document.
Version 8.3.2 (release date: Feb 2, 2022) is the foundation for the current volume forecasts for the Wasatch Front region. This forecast is available in an interactive map which also includes forecasts for the other regions of Utah from the respective RTPs and long range plans for those areas. This viewer is also linked in the resources down below.
The volume forecasts are in the process of being updated from the official models associated with the 2023-2050 RTPs and long range plans. It is anticipated that the volume forecast map will be updated by early 2024 with the results of this work.
The travel model includes the phased, fiscally-constrained 2019-2050 RTP roadway and transit projects and the official traffic analysis zone (TAZ)-level socioeconomic forecasts for the Region. WFRC and MAG have calibrated the model’s parameters to reflect local travel behavior patterns reported in the Utah Travel Study household survey (trip rates, trip lengths, time of day of trip, mode of travel, etc.) and validated the model’s results with observed travel conditions (transit ridership, roadway volumes, and roadway speeds) for the model’s base year, 2015. Additional processes, including external review, are used to validate the reasonableness of future year travel projections.
To request a copy of the current TDM, please contact Suzie Swim.
Real Estate Market Model
The current shared WFRC/MAG Real Estate Market Model (REMM) version is 2.x. The WFRC/MAG REMM relies on best available resources to project future residential and employment-related development activity using the UrbanSim modeling platform. In order to accurately model future years, REMM is first calibrated to best reflect the base year of the adopted RTP, currently 2019. Critical inputs to REMM’s consideration of available land and profitability of new and redevelopment activity include:
- A region-wide parcel land use and valuation database;
- An inventory of local government general plans;
- The results of a multi-year scenario-based visioning exercise;
- A synthesized household population dataset for the model’s base year (2015) based on Census data;
- Address geocoded employment totals from the Utah Department of Workforce Services (DWS);
- County-level employment and population control total projections, sourced from the University of Utah’s Kem C. Gardner Policy Institute;
- Public and private sector expert advisors; and
- ‘Physical constraint’ map layers that depict areas where future development is prohibited or not practical due to steep terrain, wetlands, mining, or public lands (formal designations or ownership).
REMM produces TAZ-level socioeconomic projections that are reviewed by staff and external experts for plausibility. The socioeconomic projections are packaged with the TDM files but are also available as GIS layers that can be viewed, downloaded (.shp, .gdb, .kml, or .csv), or used as web services from the data.wfrc.org open data website.
These household and job distribution projections inform future trip generation in the regional TDM. And in turn, REMM factors travel accessibility derived from the travel model into its predictions of land development activity.
WFRC and MAG hosted a expert peer review of REMM and its related processes in August 2019. Three land use modelers from comparable MPOs (Albuquerque, Detroit, Phoenix) were provided with REMM 1.0 documentation in advance of a 2 day in-person review seminar that featured presentations from and discussion among the panelists and WFRC/MAG area stakeholder agencies. The review concluded that REMM is well within best practices for land use modeling and recommended potential future areas of enhancement (view 2019 REMM Peer Review report).
Related Resources:
WFRC employs sophisticated transportation and land use modeling tools to provide decision-makers, agency staff, and the public with reliable, insightful forecasts from which to analyze future scenarios and best inform planning for our Region.
As transportation and land use are mutually dependent, forecasting for both of these systems 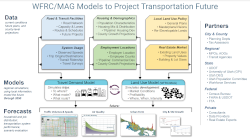 must work in tandem in order to optimally support the development, selection, and prioritization of future transportation projects to meet future needs. Similarly, the integrated WFRC/MAG modeling tools can be critical for exploring local land use policies such as those that promote urban and local centers, and the impact of our urban systems on air quality.
must work in tandem in order to optimally support the development, selection, and prioritization of future transportation projects to meet future needs. Similarly, the integrated WFRC/MAG modeling tools can be critical for exploring local land use policies such as those that promote urban and local centers, and the impact of our urban systems on air quality.
Projected measures produced with assistance from transportation and use models include:
- future population, household, and employment distributions;
- travel patterns and mode share;
- future vehicle and transit volumes and their relationship to the capacity of existing facilities and services;
- travel times and comparative accessibility to workplaces and other key destinations; and
- key inputs to air quality mobile-source emission models
Developing and maintaining travel and land use models is a best practice for regional planning. But it also fulfills requirements and expectations needed to continue to receive our Region’s share of federal transportation funding. Accordingly, WFRC’s modeling processes comply with federal law (FAST Act, MAP21, and Clean Air Acts) as well as guidance provided by the US Department of Transportation (USDOT), the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), the Federal Transit Administration (FTA), and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
For tools and web resources related to the WF-TDM and REMM, please navigate to the Model Resource Gallery.
The Wasatch Front TDM and REMM are updated every four years in sync with the four-year RTP cycle. These models serve the Salt Lake City-West Valley City, Ogden-Layton, and Provo-Orem Urbanized Areas. For more information on any of the above, contact the WFRC Analytics Group.
